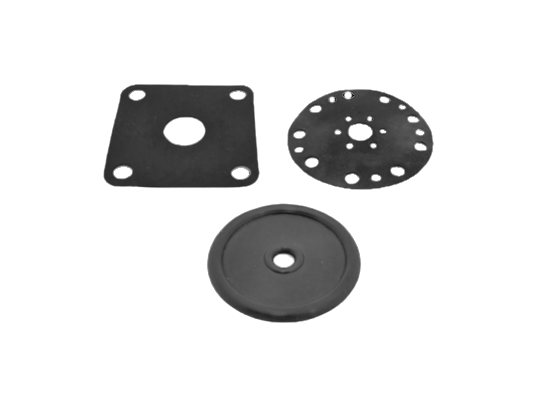
Diaphragms
Membranes are developed for special requirements and have different functions such as separation or control.
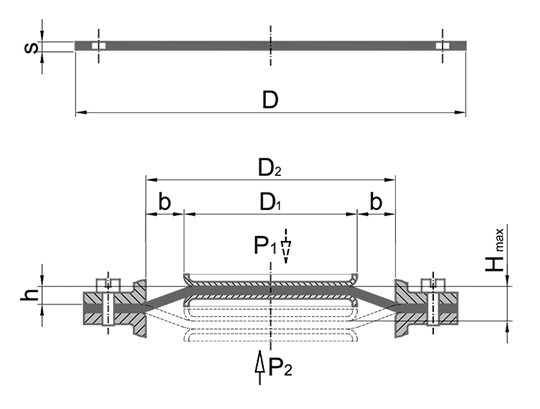
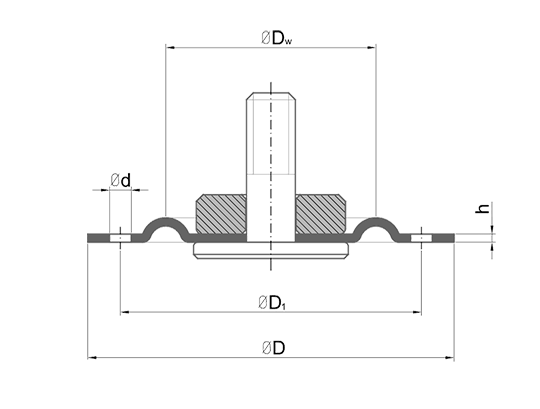
There are several different types of membranes: flat, plate, curved and roll membranes. The main difference between the basic types of diaphragms is: casing diameter – Dc, effective diameter – Dw, absolute stroke – Hmax, permissible working pressure and direction of action of working pressure.
DESCRIPTION
Flat diaphragms allow pressure on both sides.
They can be manufactured in rubber or with fabric reinforcement.
They have the same effective area on both sides.
They have limited stroke:
Hmax ≤ 0.06 x D2 for regulatory function
Hmax ≤ 0.1 x D2 for pump function
APPLICATIONS
Pump
Regulation
Control and mesurement
DESCRIPTION
Plate diaphragms allow pressure on both sides.
They can be manufactured in rubber, with fabric reinforcement or rubber with barrier foil of PTFE, PI
They have the same effective area on both sides.
They have sealing function.
They have average stroke:
Hmax ≤ 0.24 x Dw
Long working life
APPLICATIONS
Dosing
Actuator
Regulation
Control and mesurement
Valve
DESCRIPTION
Folded diaphragms allow pressure in loop direction.
They can be manufactured in rubber or with fabric reinforcement.
They have small effective surface change.
They have sealing function.
They have average stroke:
Hmax ≤ 0.19 x Dw
Very long working life
APPLICATIONS
Dosing
Regulation
Control and mesurement
Valve
DESCRIPTION
Roll-diaphragms allow pressure only on one direction.
They can be manufactured in rubber or with fabric reinforcement.
They have a few changes in effective area.
They have sealing function.
They have very large stroke:
Hmax ≤ 1.1 x Dw
Long working lifetime
APPLICATIONS
Actuator
Regulation
Control and mesurement
The elastomer material used for the production of membranes depends on the influence of physical, thermal and chemical loads during exploitation. Good viscoelasticity and high adhesion to metal or cloth inserts and low gas permeability value are required from the material.
For higher loads, one-way or two-way pressure or the required diaphragm shape, versions with a fabric insert are possible.
| EPDM – Ethylene propylene-diene | Is a common diaphragm material used with cold and warm water, hot water and steam up to 130/140 °C. Special qualities are available for use in the foodstuffs industry. This material is not resistant to oil. |
| NR – Natural rubber | Is characterised by high strength, elasticity and flexibility when cold. This material is not resistant to oil. |
| IR – Butyl rubber | Diaphragms made of butyl rubber have the lowest gas permeability and are suitable for applications such as gas accumulators and are also resistant to hydraulic brake fluids |
| NBR – Acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber | This is the standard material for all diaphragms that are loaded with compressed air carrying traces of mineral oils. NBR rubber with a higher acrylonitrile content are used if sealing against natural gas, propane and mineral oil are desired. |
| HNBR – Hydrogenated NBR rubber | Hidrogenated nitrile rubber has a higher physical strength, higher resistance to heat and less abrasion than NBR. It is used for application , for example, as diaphragm for hydraulic oil accumulator or as a oil pump diaphragm and has operating conditions from 30°C to+ 150°C. |
| FPM – Fluoro rubber |
FPM rubber has high thermal and chemical resistance and has low gas permeability at room temperature. It is the preferred material for diaphragms in vacuum technology and for applications with gases and fluids with a high aromatic level “super fuels”. |
| FVMQ – Fluoro silicone rubber |
Is used for special requirements for applications with low temperatures and high fuel resistance. FVMQ rubber has operating conditions from -60°C to + 175°C. |
| VMQ – Silicone rubber |
VMQ rubber can be compounded to be physiologically neutral and also can be sterilised with hot air and thus be suitable for the foodstuffs industry. VMQ rubber has operating conditions from -40 °C to +200 C |
| Polyseal material code on request after mutually agreed project. |