Materials

When is an NBR seal better than one made of EPDM or FPM rubber? What is the right answer for hydraulic system sealing and what is for the beverage industry? How are the various mixtures differentiated from one another?
It’s our job to know that, because we produce the “Materials”
EPDM
EPDM can be cured with sulfur and have superior mechanical properties and inferior properties at high temperatures and vice versa when cured with peroxide.
EPDM rubber is not suitable for use with mineral oils or petroleum-based oils and greases or in gasoline and hydrocarbons.
EPDM rubber shows high media resistance to brake fluids, acids and bases, flame-resistant hydraulic fluids HFC and HFD, hot water and steam. Compounds E55520 and E5522 are recommended for this medium. Further EPDM rubber has good chemical resistance and is especially recommended for use with phosphate ester hydraulic systems.
Special compounds E5540 (black) and E5542 (white) were developed for the process industry.
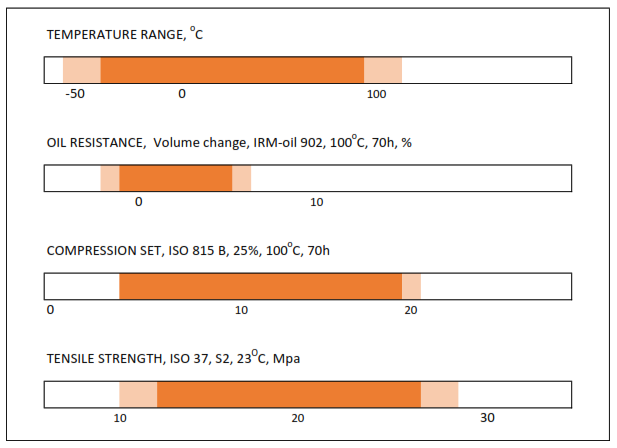
NBR
NBR is the abbreviation for nitrile butadiene rubber. The properties of NBR mainly depend on its ACN content.
The ACN content determines the balance between media resistance and low-temperature flexibility. Low ACN content produces a low glass transition temperature but also leads to greater swelling in oils and fats and vice versa if ACN content increases. This content in production of elastomers can vary and thus produce different types of the material.
Nitrile rubber exhibits superior mechanical strength with high elasticity as well as good deformation behavior in a temperature range between -30 °C and 100 °C. Our standard material N4913 and 4271
Standard compounds N7010 and N4188 were developed for low temperature applications, followed by specialty compounds N5185 and N7272 for extremely low temperature applications and applications requiring excellent fluid resistance.
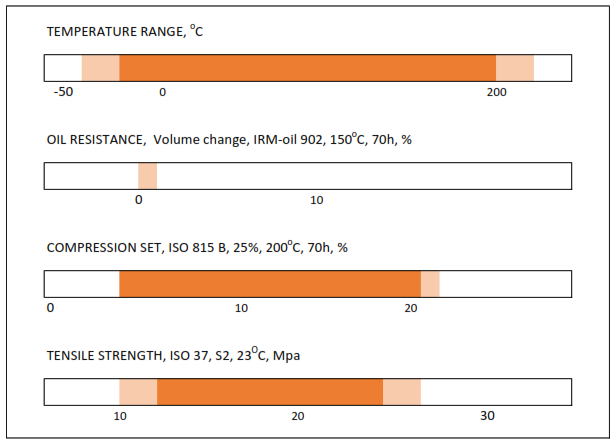
FPM
FPM seals show very good resistance to media, ozone and aging. The material is also stable on fuels, petroleum-based oils and greases, aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons.
It is unstable in relation to polar solvents: acetone, MEK, ethyl acetate, low molecular weight organic acids, e.g. acetic acid, glycol-based brake fluid, ammonia gas, amines, alkalis and superheated steam.
FPM materials are copolymers, terpolymers and tetrapolymers with varying fluorine content between 65 and 71 percent. This helps to design the FPM for specific media resistance and cold flexibility requirements.
Fluorine rubber is mainly used for seals in the range from -20 °C to 200 °C Special types of FKM are flexible even at -40 °C.
In general industry, FKM is used wherever there are high temperatures or other specific requirements in the chemical, petroleum and aerospace sectors.
Materials F9172 and F9183 are the preferred choice for standard seals such as O-rings and F9970 for process industry applications.
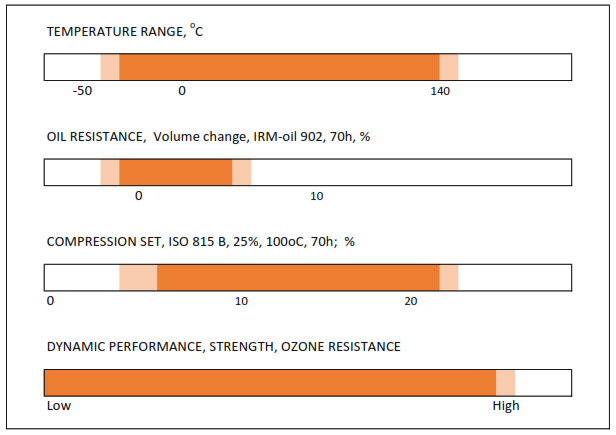
HNBR
HNBR is a synthetic polymer produced by selective hydrogenation of nitrile rubber. In this process the reactive double bonds are removed from the NBR making the molecular chain inactive to react so easily with oxygen. As a result, we have a hydrogenated material significantly more heat resistant than we had in NBR. We also have high resistance to hot water and good behavior at temperatures between -40 °C and 140 °C.
HNBR offers better wear behavior in dynamic applications.
In sealing technology, these properties enable use in applications where higher temperatures and/or mechanical strength are required. The mechanical strength of HNBR is in demand for rod and piston seals, as well as special sealing elements.
In the process industry, HNBR is an excellent solution as a material H5131 and H5144 for O-rings, clamp seals, butterfly valve seals and other rubber parts for dairies, the beverage industry and applications where there is contact with fatty media.
FEPM
A copolymer of tetrafluoroethylene and propylene, FEPM is sold under the name Aflas®.
FEPM vulcanizates show similar thermal stability to FKM elastomers, but slightly better electrical resistance and chemical resistance.
Aflas has high resistance to a wide range of chemicals such as hydraulic and brake fluids, acid gas and oil, amine corrosion inhibitors and water-based drilling fluids.
Also, high resistance to acids and strong alkalis, alcohols, steam and water, ozone and high energy radiation.
However, they are not compatible with aromatic hydrocarbons, chlorinated hydrocarbons and organic solvents.
FEPM elastomers are suitable for long-term use in air up to 225°C and short-term up to 250°C, but are limited in low temperature applications.
FEPM find wide use mainly in oilfield and chemical processing applications as O-rings, gaskets and seals. Our standard solution FP938.
TPU
Thermoplastic polyurethane deliver excellent performance even in extreme envinronments. It is formulated with the needs of the modern elastomer manufacture in mind and is ideal for the industrial applications.
TPU generally exhibit excellent tensile strength, tear and wear resistance, and provide excellent protection against oxygen and ozone. It has extensive operating temperature rangea from -40°C to 130°C and very high strength at room temperature and consistent performance to 120°C
TPU are used where high abrasion resistance, low tempwrature performance, relativly high resistance to hydrolysis and oil/solvent resistance are required, They are an ideal row material for hydraulic and pneumatic seals, gaskets and diaphragms. Our standard compounds U5002 and U5017.
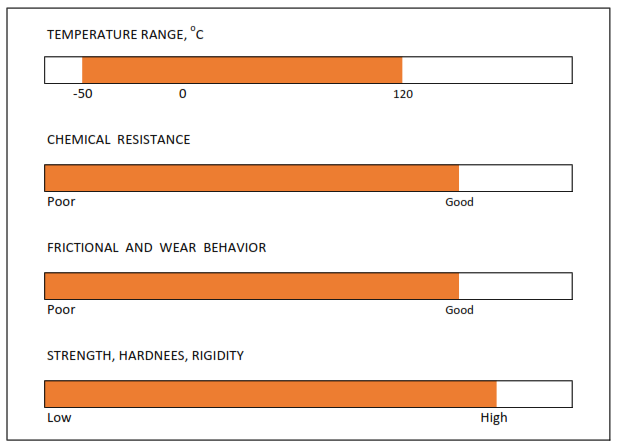
POM
POM is abbreviation for Polyoxymethylene and it is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic and is especially used as a technical plastic for precision parts.
It exibits outstanding dimensional stability, high rigidity, low coefficient of friction and high resistance to abrasion. Its mechanical properies combined with its good frictional and wear behavior make it a good choice for a wide range of technical applications. Our standard material P6221 or P6686 and fiber compound P6212.
POM has good chemical resistance, absorbs water to a low degree and threfore there are many types ideal for use in contact with foods.
Thanks to its own high crystallinity, POM exibits rigidity and can withstand great force or pressure especially in the temperature range of −50 °C to 120 °C.
PA
Polyamides materials are molding compounds on the basis of PA6, PA66 and various co-polyamides such as PA66/6 and PA610. The molding compounds are available unreinforced, reinforced with glass fibers or minerals and also reinforced with long-glass fibers for special applications.
Polyamides offer high mechanical strength, stiffnees, thermal stability and good chemical resistance. In addition, they offers good toughness at low temperatures and exhibit high resistance to wear and favorable sliding friction properties.
Owing to its excellent properties, this material has become indispensable in almost all sectors of engineering for a wide range of machine elements also is especially suited to use in the sealing area as slide bearings or guide strips and back-up rings for many of sealing elements. Our material P6020 or P6060.
PTFE
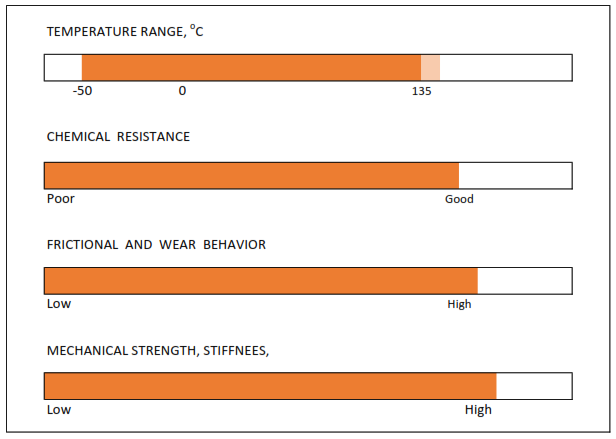
If applications do not require elastic properties, PTFE material is the right solution. It can be used in an extremely wide temperature range, from -200 °C to 260 °C.
Its resistance to media and a wide range of temperatures recommend it for use at high or low temperatures and in contact with chemically aggressive substances.
PTFE is also a physiologically inert material and is approved for contact with food and drugs.
PTFE when deformed exhibits plastic, irreversible deformation at all temperatures. It has a very low coefficient of friction compared to most known materials. These qualities make it ideal for use in dynamic seals.
PTFE is one of the most preferred materials in the process industry. The most important criteria for its selection are its extremely high purity, use in an extremely wide range of temperatures and high chemical stability in almost all media.
Sliding seals, scrapers or spring rings, then radial shaft seals and gaskets are well-known PTFE seal solutions in the industry. Our materials T1001, T1004, T1021, T1030